Fibrosis of the Liver: 10 Signs and Symptoms of Liver Fibrosis
Liver fibrosis happens when scar tissue takes the place of healthy liver cells because of long-term damage or disease. This condition can develop slowly, often without noticeable symptoms, until the liver is seriously affected. Spotting the signs early can help slow down or stop further damage. If fibrosis gets worse, it can lead to cirrhosis, a serious disease that might require a liver transplant. Learning about the symptoms and seeing a doctor early can help protect your liver health.
Feeling Tired and Weak All the Time
One of the first signs of liver fibrosis is constant tiredness. People with this condition often feel exhausted even after a full night’s sleep. This happens because the liver helps control energy levels, and when it is damaged, energy production slows down. Also, toxins can build up in the blood, making you feel even more drained and weak.
Losing Weight Without Trying
If you’re losing weight without meaning to, it could be a sign of liver problems. A damaged liver has trouble processing nutrients, which can cause loss of appetite and muscle weakness. The body’s metabolism may also change, making it hard to maintain a healthy weight even if you eat normally. A lack of nutrients can lead to dizziness and a weaker immune system.
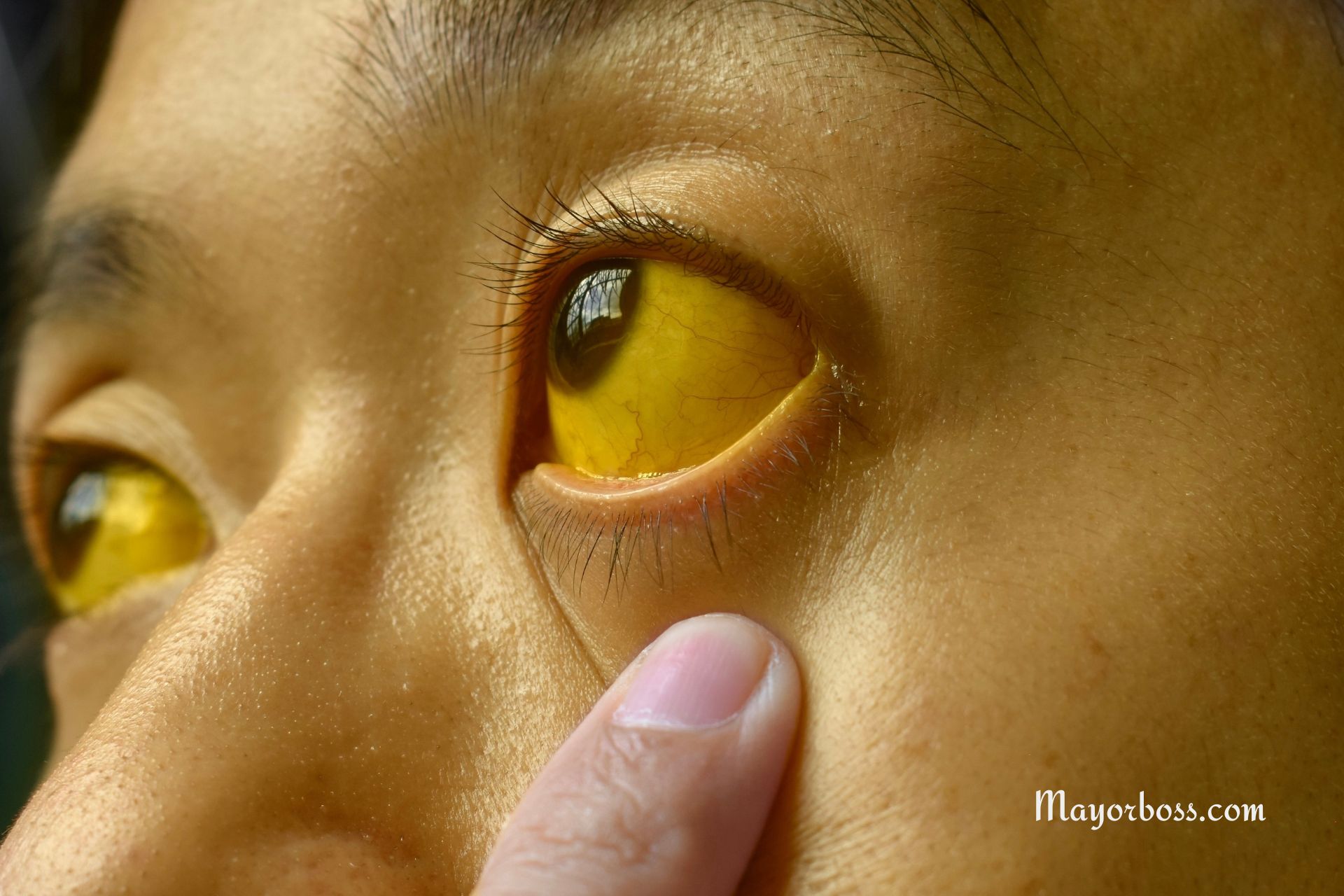
Yellow Skin and Eyes (Jaundice)
Jaundice happens when bilirubin, a yellow substance made by the liver, builds up in the blood. This makes the skin and eyes turn yellow. It can also cause dark urine and severe itching. In serious cases, jaundice is a sign that the liver is in trouble and needs immediate medical attention.
Stomach Pain or Discomfort
As liver fibrosis worsens, it can cause pain or discomfort in the upper right side of the belly. This happens because the liver becomes inflamed or swollen. Some people feel full or bloated, especially after eating. This symptom can be confused with indigestion or heartburn, which may delay diagnosis.
Swelling in the Legs and Belly
Liver fibrosis can lead to fluid buildup in the body, causing swelling in the legs, feet, and ankles. In some cases, fluid collects in the belly, making it look swollen. This happens because the liver can’t regulate blood pressure and protein levels properly.
Bruising and Bleeding Easily
A damaged liver makes fewer proteins that help blood clot. This means you may bruise easily or have nosebleeds and bleeding gums. Small cuts might take longer to stop bleeding. In severe cases, internal bleeding can happen, which is dangerous.
Dark Urine and Pale Stools
Changes in urine and stool color can be a warning sign. Dark urine means too much bilirubin is in the blood, while pale or clay-colored stools mean the liver isn’t making enough bile. Some people may also have oily or greasy stools, which show that the body isn’t digesting fats properly.
Feeling Nauseous and Having Stomach Issues
People with liver fibrosis often experience nausea, vomiting, bloating, and indigestion. The liver helps break down fats, so when it is damaged, it can cause stomach discomfort. Some people also develop acid reflux or feel bloated after eating fatty foods.
Trouble Thinking Clearly or Forgetfulness
Liver fibrosis can cause hepatic encephalopathy, a condition where toxins build up in the brain. This can lead to memory problems, trouble focusing, and mood changes. In serious cases, people may become confused, have slurred speech, or even go into a coma. Early treatment with medication and diet changes can help control these symptoms.
Itchy Skin Due to Bile Buildup
Liver fibrosis can cause severe itching, also called pruritus, because bile salts build up in the skin. This itching can be widespread and get worse at night. It can be extremely uncomfortable and affect sleep and daily activities.
Summary
Liver fibrosis develops slowly, so catching it early is important. Constant fatigue, yellow skin, swelling, nausea, and trouble thinking are signs that should be taken seriously. If you notice these symptoms, see a doctor for tests and evaluation. Getting treatment early may slow or stop liver damage. Also, lifestyle changes like eating a balanced diet, avoiding alcohol, and managing conditions like hepatitis can help protect the liver.
