Visible Signs of Cervical Cancer
Cervical cancer happens when strange cells grow in the cervix. The cervix is the lower part of the uterus, which connects to the vagina. It is often caused by certain types of human papillomavirus (HPV). In the early stages, many women with early cervical cancer usually do not have clear symptoms. Yet, some signs might be noticeable.
When caught early, cervical cancer can be treated successfully and often cured. That’s why regular Pap tests are important. Women should also know the warning signs so they can talk to a doctor if needed. Here are some signs that could mean cervical cancer.
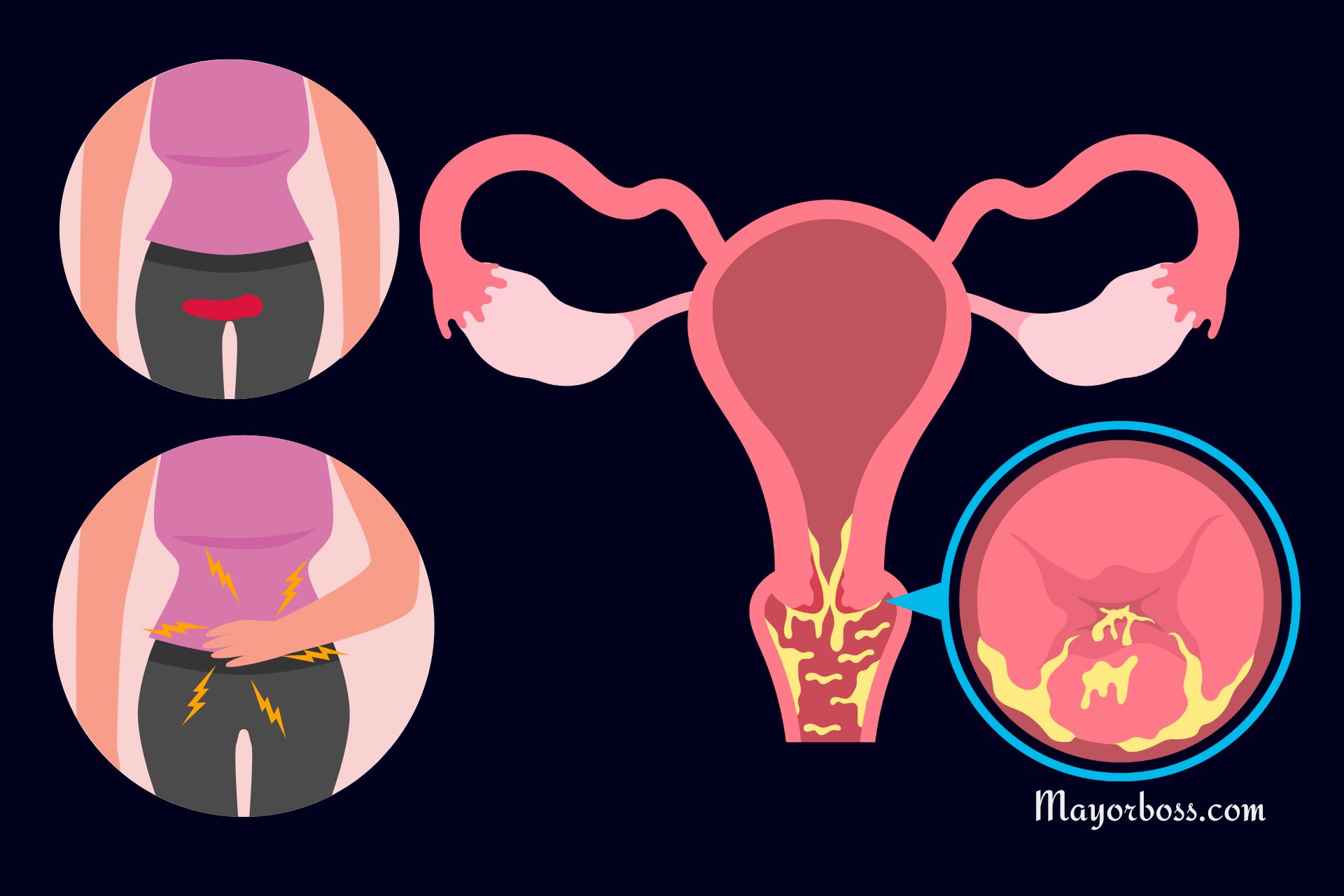
Unusual vaginal bleeding
A common sign of cervical cancer is bleeding from the vagina that does not follow your normal menstrual cycle. This can happen after sex or between periods. Bleeding after menopause (when you no longer have monthly periods) can also be a warning sign. Any unexpected bleeding is a reason to talk with a healthcare provider.
Bleeding between periods
If you notice spotting or light bleeding between your regular monthly periods, it could mean there are changes in the cervix. Bleeding like this can have other causes, so it is wise to see a doctor to make sure nothing serious is going on.
Postcoital bleeding
Some people have bleeding after sex. This might happen if there is a tumor or abnormal tissue on the cervix that gets irritated. While other conditions can cause bleeding after sex, it is best to get checked to find out the exact cause.
Unusual vaginal discharge
Another sign of cervical cancer is a change in vaginal discharge. It might have a strong odor or look watery. It could be thick or even have some blood in it. Many things can cause unusual discharge, but you should still see a doctor to learn what is going on.
Pelvic pain and discomfort
Abnormal cells in the cervix may cause pain in your lower belly or back. Some people feel mild cramps or pressure. Others might feel sharp pain. You might also feel pain when you have sex or when you go to the bathroom. These issues alone do not mean you have cervical cancer, but you should see a professional if the pain lasts or gets worse.
Pain during intercourse
Pain during sex, also called dyspareunia, can be another sign. Tumors or inflamed areas on the cervix can cause pain. Because many conditions can lead to discomfort during sex, it is best to let a doctor figure out the cause.
Chronic fatigue
If there is internal bleeding from cervical cancer, it might lower the number of red blood cells in your body. This can lead to anemia. Anemia often makes you feel weak or very tired, even if you are getting enough rest.
Loss of appetite and weight changes
Advanced cervical cancer can sometimes lead to weight loss. People may lose interest in eating and have trouble keeping up their normal diet. If you notice a drop in appetite or a steady loss of weight without trying, you should see a doctor.
Swelling in the legs
A tumor in the cervix can press on nearby tissues or block the flow of fluids. This can lead to swelling in the legs. You might also have pain or trouble walking. While there are many reasons for leg swelling, any sudden swelling that does not go away should be checked by a healthcare professional.
When to see a doctor
Finding cervical cancer early can lead to better treatment results. Talk to a doctor if you have abnormal bleeding, a new kind of discharge, or pelvic pain. These signs may have other causes, but it is still important to find out what is going on. Often, doctors start by doing a pelvic exam and might do more tests if needed.
Diagnostic tests
Pap test
A Pap test looks for abnormal cells in the cervix. If the test finds unusual cells, you may need other tests to see if these cells are cancerous.
HPV test
Since HPV is the main cause of cervical cancer, doctors often do an HPV test with the Pap test. If you have a high-risk type of HPV, you may need more checkups.
Colposcopy
A colposcopy allows the doctor to get a closer look at your cervix with a special instrument. The doctor may take a tiny sample of tissue (a biopsy) to send to a lab. The results help decide the next steps in treatment.
Treatment approaches
Treatment depends on how far the cancer has spread. Surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy are common choices. In the early stages, a simple surgery might remove the cancer. In later stages, you might need a mix of different treatments. The doctor will also consider your overall health and your plans for having children in the future.
Preventive measures
Regular screening is the best way to catch cell changes early. Many experts suggest a Pap test every three years starting at age 21. Getting the HPV vaccine can help prevent infections that lead to cervical cancer. Practicing safe sex and avoiding smoking can also lower your risk.
Takeaway
Visible signs of cervical cancer often include unusual bleeding, discharge, or pain in the pelvic area. These might be easy to miss at first. Because early treatment leads to better results, it is important to see a doctor right away if you notice any odd changes. Regular Pap tests, HPV tests, and healthy lifestyle habits can help reduce your chances of developing cervical cancer. If you have concerns, do not hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional.
