Long-Term Side Effects of Tylenol (Acetaminophen)
Tylenol, also known by its generic name acetaminophen, is a widely used over-the-counter pain reliever and fever reducer. While it’s generally considered safe when taken as directed, long-term use or high doses can lead to a range of side effects. Understanding these potential risks is essential for anyone using acetaminophen regularly. Let’s explore the long-term side effects of Tylenol.
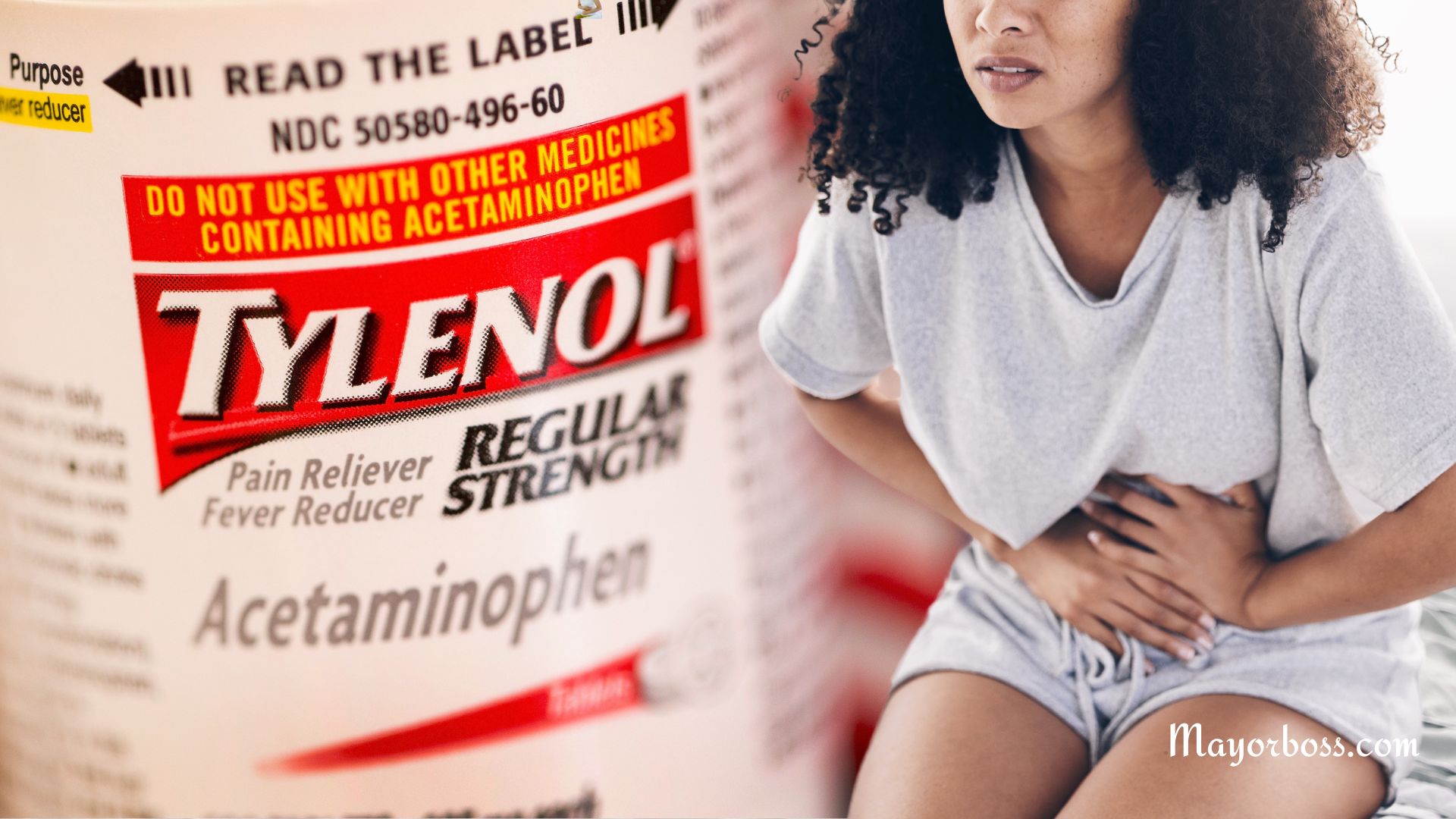
Liver Damage Is One of the Most Serious Risks of Long-Term Acetaminophen Use
One of the most significant concerns with long-term acetaminophen use is the likelihood of liver damage. The liver processes acetaminophen, and excessive amounts can overwhelm its capacity, leading to acute liver failure. The risk increases dramatically with high doses or if combined with alcohol. Symptoms of liver damage may include:
- Nausea or vomiting
- Abdominal pain, especially in the upper right side
- Fatigue or weakness
- Jaundice, which is a yellowing of the skin and eyes
If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s crucial to seek medical attention promptly.
Long-Term Use of Acetaminophen May Lead to Kidney Problems
Chronic use of acetaminophen can also impact kidney function. Studies have indicated that people who regularly use acetaminophen over long periods may be at a significantly higher risk for chronic kidney disease (CKD). Kidney damage may not present immediate symptoms but can develop over time, leading to problems like:
- Decreased urine output
- Swelling in your legs, ankles, or feet due to fluid retention
- Fatigue and weakness
If you have a history of kidney disease or other risk factors, it’s essential to discuss your acetaminophen use with your physician.
Gastrointestinal Issues Can Arise from Prolonged Acetaminophen Usage
While acetaminophen is usually more light on the stomach compared to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen, long-term use can still lead to gastrointestinal issues. These may include:
- Nausea or vomiting
- Stomach pain or discomfort
- Diarrhea
These symptoms can arise from the way acetaminophen interacts with the stomach lining and can indicate that your body is reacting negatively to prolonged use.
Prolonged Use of Acetaminophen May Affect Your Heart Health
Some research suggests that long-term use of acetaminophen may have an impact on cardiovascular health. While more studies are needed, there is evidence to indicate that chronic use may increase the risk of heart problems, including:
- Hypertension (high blood pressure)
- Heart attack
- Stroke
If you have existing heart conditions or risk factors, it’s essential to monitor your acetaminophen intake and consult your doctor about safer pain relief alternatives.
Allergic Reactions Can Occur with Extended Use
Although uncommon, some individuals may experience allergic reactions to acetaminophen, especially with long-term use. Symptoms of an allergic reaction may include:
- Rash or hives
- Itching or swelling, particularly of the face, tongue, or throat
- Feeling or being sick
- Severe dizziness or difficulty breathing
If you experience any of these symptoms after taking acetaminophen, seek medical help immediately.
Potential Effects on Blood Pressure
Emerging research indicates that long-term use of acetaminophen may influence blood pressure levels. Some studies have shown a potential association between chronic acetaminophen use and increased blood pressure, particularly in older adults. Monitoring your blood pressure regularly can help identify any changes if you’re using acetaminophen frequently.
Risk of Overdose Increases with Long-Term Use
Repeated long-term use of acetaminophen can heighten the risk of accidental overdose, especially if you’re unaware of how much you’re taking. Symptoms of an overdose can include:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- Confusion
- Jaundice
If you think you may have taken too much acetaminophen, it’s crucial to seek medical help right away.
Recommendations for Safe Acetaminophen Use
To minimize the risks associated with long-term acetaminophen use, consider the following recommendations:
- Follow dosage instructions: Always adhere to the recommended dosage on the label or your physician’s advice.
- Limit alcohol consumption: Avoid drinking alcohol while taking acetaminophen, as it can increase the risk of liver damage.
- Monitor for symptoms: Keep an eye on any unusual symptoms you may experience while taking acetaminophen regularly.
- Consult your doctor: If you find yourself relying on acetaminophen for an extended period, discuss alternative pain relief options with your physician.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you experience any of the following symptoms while using acetaminophen, seek medical help immediately:
- Jaundice: Yellowing of the skin or eyes.
- Severe Abdominal Pain: Especially in the upper right side.
- Unusual Fatigue: Persistent and unexplained tiredness.
- Signs of Allergic Reaction: Rash, itching, swelling, or difficulty breathing.
- Changes in Urination: Reduced urine output or dark-colored urine.
Conclusion
While Tylenol (acetaminophen) is a commonly used and generally safe medication for pain relief and fever reduction, it’s essential to be aware of the potential long-term side effects. Liver damage, kidney problems, gastrointestinal issues, cardiovascular risks, allergic reactions, and the potential for overdose are all serious concerns associated with prolonged use. If you regularly use acetaminophen, make sure to monitor your health closely and consult your healthcare provider for advice.
